Developing a first-in-class subcutaneous injectable as a non-surgical alternative to treat fat disorders
|
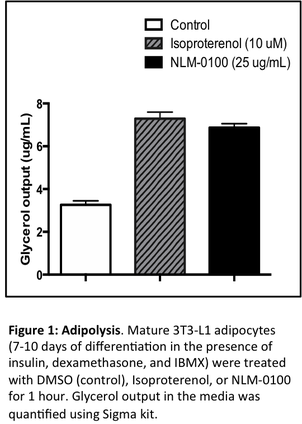
In the rare metabolic disease space, we are developing a subcutaneous injectable to treat Dercum’s disease, a disorder characterized by the slow formation of multiple, painful growths of fatty tissue (lipomas) that are found just below the surface of the skin. Dercum's disease mainly occurs in adults and more women are affected than men. In some cases, affected individuals may also experience weight gain, depression, lethargy, and/or confusion. It is estimated that few hundred patients exist with this condition in United States. No specific treatment exists for Dercum's disease. Various painkillers (analgesics) have been tried with limited effectiveness. Surgical excision of fatty tissue deposits around joints may temporarily relieve symptoms although recurrences often develop. Clearly, there is an unmeet need for this disease. At Nivarta, we have identified a protein that can shrink lipomas through fat lipolysis when injected subcutaneously. It has been shown to induce significant lipolysis in rodent models of obesity, mouse 3T3L1 adipocytes (Figure 1), and human primary adipocytes. In addition, the protein has been shown to inhibit lipid biosynthesis in adipose tissue raising the possibility that recurrence of lipoma formation may be curbed. Towards next steps, we are testing a proprietary hydrogel formulation in collaboration with Novozymes to extend the release and retention time of the protein when injected subcutaneously.
USEFUL LINKS: Learn more about Dercum's http://www.lipomadoc.org/dercums-disease.html http://fatdisorders.org |